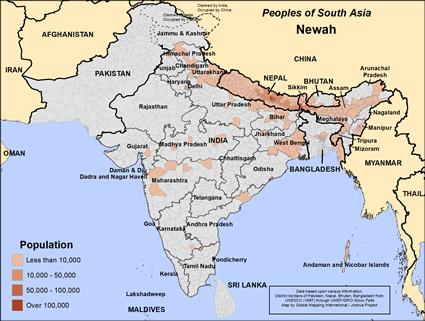
The Newar, (AKA, Newah) one of the most cultured ethnic groups in Nepal, were the country's earliest inhabitants. An important part of the Newah civilization was trade; they were the ones who organized trade between India and Tibet.
For about 1,000 years the Newah civilization blended aspects of Hinduism from the south and Buddhism from the north. There are myths regarding the creation and origin of the Kathmandu Valley where the Newah people developed a prosperous civilization. This civilization was conquered by the Gorkha Kingdom in 1769. Their heart language is Newah, a Tibeto-Burman language that has borrowed many words from Sanskrit, Maithili and Nepali. There are several dialects of their language. Most of the younger generation, however, speak Nepali, the common trade language of Nepal.
Though the Newah are scattered throughout Nepal, they are primarily concentrated in the Katmandu Valley. There is a smaller number of them northern India, Bangladesh and Bhutan.
Newah society is traditionally caste-based (as in India) with distinct caste-systems being centered in each of the old royal cities of Kathmandu, Lalitpur and Bhaktapur. Traditionally intermarriage was largely restricted to one's fellow caste members and boys were expected to follow the occupation of their fathers. Today the modern economy means there is theoretically freedom to follow almost any trade, but inter-caste marriage is still widely frowned upon if not seriously punished.
Trade and agriculture have a longstanding history among the Newah people. Newah sons take over the occupation of their fathers. That could mean sons learn farming, a trade, a craft or how to function well as a merchant. Newah societies are patrilineal, which means that the line of descent is traced through the males. Members of the same family line generally worship the same gods. Marriages are almost always arranged by the parents, and they use a mediator to complete the formalities.
In their free time, the Newah people enjoy indoor sports and board games. These games often involve gambling. There are some outdoor sports like soccer, but this is usually limited to urban areas.
Hinduism, Buddhism, and traditional ethnic beliefs are all a part of the Newah's religious lives. Some Newahs are self-consciously Hindu and others self-consciously Buddhist, but most would not recognize the distinction. For them it is more important to follow the traditions of the ancestors than it is to argue about religious affiliation or doctrine. Newahs worship a multitude of gods, many of which are local gods and others are more clearly identified with the prestigious deities worshipped to the south, especially Shiva. They also believe in the existence of demons, hostile spirits the dead, ghosts and witches. Traditional practices include the digu dya rituals, in which they feed frogs after rice planting. They think that cremation grounds, crossroads and huge stones are often haunted. They believe diseases are caused by the ill will of the "mother goddess," witchcraft or evil spells. Treatments include reciting incantations, making offerings to the gods, and using herbs and other medicines.
Portions of the Bible and several other Christian resources have been translated into Newah language. Who will call their attention to these? The Newah people love music and art. They need Christ followers to use these to take the gospel to them.
Pray that the sheer wonder of knowing Jesus and the impact he has on their lives and the joy he brings spur believers to share Christ with the Newah people in India.
Pray the hearts of the Newah people would be stirred by a sovereign work of the Holy Spirit readying them for the time when they hear the gospel message being shared with them.
Pray they will experience dreams and visions of Jesus leading them into a saving relationship with him.
Pray for an unstoppable movement to Christ among the Newah people in India.
Scripture Prayers for the Newah in India.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newar_people
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/who-are-the-newar-people.html
https://www.britannica.com/topic/Newar
| Profile Source: Joshua Project |