The Mon are one of Asia's ancient peoples. They were known as great traders who did business with India and Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) as far back as the third century BC. Sri Lankan monks introduced Buddhism in the fifth century, strongly shaping Mon identity ever since. According to Mon oral traditions, a global flood once destroyed the old earth and its inhabitants, and the few survivors became the progenitors of the human race: “Torrential rain began to fall on the whole earth, until the flood rose as high as the abode of the gods. After the rains there came a wind that blew for months and years, drying up the water until the new earth came into being.”
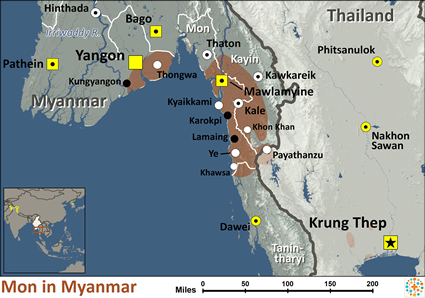
Location: More than 1.1 million Mon people are distributed across a widespread area in southern Myanmar, with most living in the five states of Mon, Kayin, Kayah, Tanintharyi, and the Ayeyarwady River delta of Bago Region. The original Mon kingdom of Suvannabhumi (“The Golden Land”) consisted of three states including Haripunjaya in Thailand, where Mon customs are still observed more closely than in Myanmar. More than 120,000 Mon people still reside in Thailand today.
Language: Mon, which is rare in Asia for being a non-tonal language, is a key component of the Austro-Asiatic family and is distantly related to the Khmer language of Cambodia. After nine centuries of conflict with the Burmese, the Mon gradually lost their culture and language. Today, few Mon people under 40 can read their own script, although most elderly people and those living in rural communities can still speak their mother tongue.
Mon civilization flourished between the fifth and eighth centuries, covering much of today's southern Myanmar and central Thailand. Mon history records constant wars with the Burmese until they were finally subdued in 1757. Their kingdom was demolished, and many Mon were pushed into southern Myanmar and east into Thailand. Mon State was established in 1974, but it has done little to pacify the Mon. Unrest has continued as the Mon National Liberation Army continued to fight for independence.
Much of Mon life revolves around Buddhist temples and monasteries, which also serve as schools and community centers. Most boys begin to serve as novice monks at around ten years of age. When they turn 21 they may choose to make a lifetime commitment as monks, while females can become nuns. After birth, “Mon mothers and babies are bathed and smeared with turmeric mixed with water. The baby's shoulder and hip joints are set, as the Mon believe that they are not properly set in place at birth."
The Mon are acknowledged as the first Buddhists in Southeast Asia. They gave the region its first alphabet, built on the Indic-based Pali script. Today the vast majority of Mon people identify as Buddhists, although animistic practices still have a place in everyday Mon life. People “give offerings to many spirits and observe several kinds of taboos. Buddhist monks are often consulted for advice about the supernatural, and they also act as astrologers.”
An American missionary from Vermont, James Haswell, arrived in Burma in 1836 and spent much of the next 40 years laboring among the Mon. Although he translated and printed 3,000 copies of the New Testament in 1847, the Mon showed little interest in Christianity, and more than six decades later it was reported: “Quite a number of these New Testaments still remain on the shelves of the Baptist Mission press.” In the 1931 census, only 808 Mon people were Christians and the rest Buddhists. By 1970, after more than 130 years of outreach, a mere 1,219 Mon believers belonged to Baptist churches in Myanmar, and today it is estimated that just one percent of Mon are Christians. Although the full Mon Bible was published in 1928, it was last printed in 1951 due to the script becoming increasingly obsolete.
Scripture Prayers for the Mon in Myanmar (Burma).
| Profile Source: Asia Harvest |