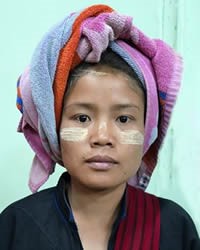
The Pa-O are called Taungthu by the Burmese, which means “hill people.” The British colonial government called them Black Karen because most Pa-O women wear black or dark blue dresses and their language is related to Karen varieties. Many Pa-O do not even know of this connection to the Karen, however, and consider themselves a unique people group. The 1901 census of Burma returned a population of 68,301 Pa-O people, which increased to 225,822 three decades later. Of those, only 320 identified as Christians and the rest were Buddhists.
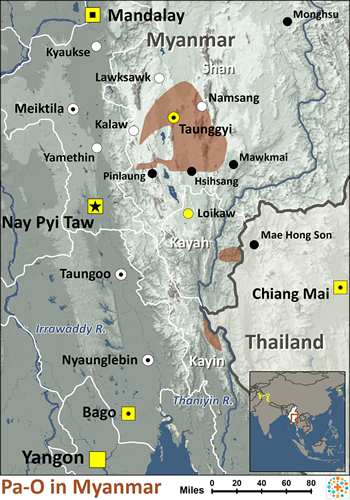
Location: Approximately 870,000 Pa-O people live in a widespread area of Myanmar, with most concentrated in southern Shan State. They are the second most numerous ethnic group in the state after the Shan themselves. Many Pa-O are concentrated around Taunggyi and Kalaw, while Pinlaung Township is the seat of the Pa-O Self-Administered Zone, which was created in 2010. Lesser numbers of Pa-O are distributed across four other areas of Myanmar, including Mon State, Karen State, Kayin State, and the Bago Region. An additional 900 Pa-O people live in Thailand, where they inhabit four villages in Mae Hong Son Province. The Pa-O in Thailand fled Myanmar in 1975 because of the terrible social upheavals and human rights abuses committed by the military junta.
Language: Pa-O, a Tibeto-Burman language with five dialects, is widely used by all ages of Pa-O people, and most are bilingual in Burmese and Shan. The Pa-O have adopted the Burmese script for writing. Pa-O is spoken as a second language by the Danau and Lahta tribes.
The Pa-O believe that their ancestors “fled north to Shan State from the Mon City of Thaton, in Lower Burma, after the overthrow of the Mon King Manuha in the 11th century by King Anawrahta of Pagan.” This defeat took place in 1057. During the current Myanmar civil war, thousands of Pa-O youths joined the Pa-O National Defence Force to fight against the Burmese junta. In February 2023, fighting in Pinlaung forced more than 5,000 villagers to flee for their lives, but a few weeks later, on March 11, Burmese troops massacred more than 30 civilians who had taken refuge inside a Buddhist monastery in the village of Nanmeng.
According to Pa-O legend, long ago “a dragon mother laid three eggs, the first of which gave birth to the Karen people, the second the Pa-O, and the third the Kayah and Padaung. The Pa-O derive their name from the vernacular word Pa-U, which means ‘helped during birth’.” One way the Pa-O tale of their origins is shown today is in their women’s clothing. Their “colorful, conspicuous turbans represent the head of the female dragon, and their darker, four layers of clothing represent her numerous scales.”
While most Karen groups in Myanmar are either animists or Christians, the Pa-O have been a strong Buddhist group for many centuries, with their faith dominating every area of their lives and communities. Pa-O families “consider ordination as a novice even greater merit than ordination as a monk. During the first day of the novice ordination ceremony, called poi sang long, the sounds of drums, gongs, and cymbals echo between the mountain ridges, when boys with shaved heads are taken from their homes to the temple…. They still retain animist beliefs to some extent. They worship the house and tree spirits, and spirit shrines are located outside villages or near pagodas, where offerings can be made.”
A mere 1,700 (0.2%) of Pa-O people are estimated to be Christians today. Most Pa-O are proud to be Buddhists who have steadfastly rejected all efforts to evangelize them. Missionaries first translated Scripture portions into Pa-O in 1912, but generations of Pa-O people passed into eternity before the New Testament was published in 1961 and the full Bible was finally completed in 2024.
Scripture Prayers for the Pa-O in Myanmar (Burma).
| Profile Source: Asia Harvest |